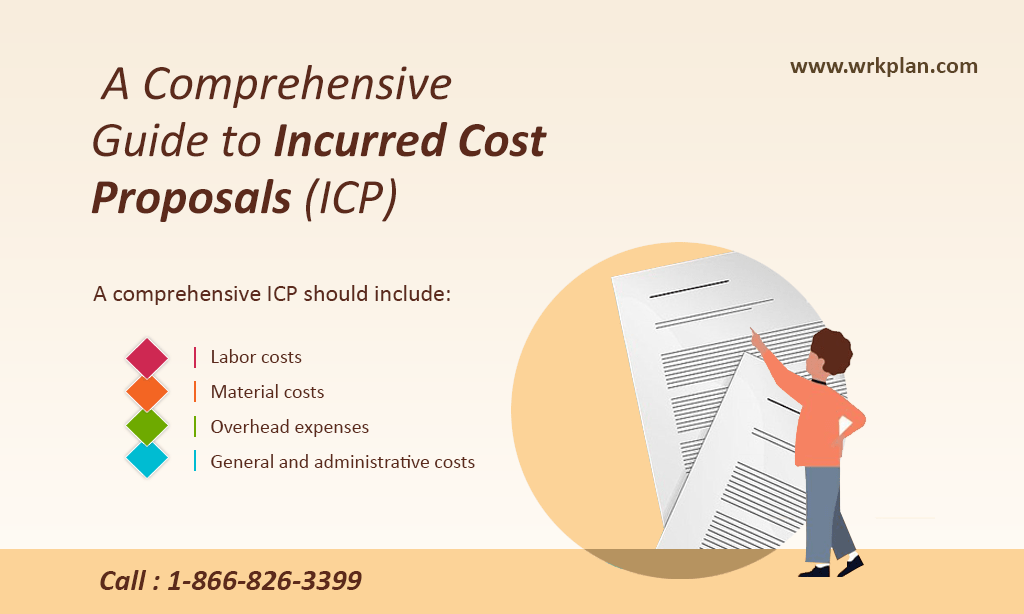
A KPI (Key Performance Indicator) tree is a graphical representation of the performance measures that are critical to the success of an organization or project. It is a hierarchical structure that shows how KPIs at different levels are linked and how they contribute to the overall objectives of the organization.
At the top of the KPI tree, you will find the ultimate goal or objective that the organization is trying to achieve. This could be something like increasing revenue, reducing costs, or improving customer satisfaction. The KPIs that are most directly linked to this goal will be located just below it in the tree.
As you move down the tree, you will see more specific KPIs that are used to measure the performance of various processes or functions within the organization. These KPIs may include things like sales growth, customer retention, or production efficiency.
The KPI tree is a useful tool for organizations because it provides a clear visual representation of how performance measures are related to each other and to the overall goals of the organization. It can also help to ensure that everyone in the organization is working towards the same goals and that everyone understands how their individual efforts contribute to the success of the organization as a whole.
There are several reasons why an organization might use a KPI tree:
- Clarity and focus: A KPI tree can help to clarify the overall goals of an organization and ensure that everyone is focused on achieving them. By breaking down the ultimate goal into smaller, more specific KPIs, it becomes easier to understand what needs to be done to achieve success.
- Alignment: A KPI tree can help to align the efforts of different teams and individuals within an organization. By showing how different KPIs are related to each other and to the overall objectives of the organization, it becomes easier to ensure that everyone is working towards the same goals.
- Monitoring and measurement: A KPI tree provides a framework for monitoring and measuring performance. By identifying the most critical KPIs and tracking them over time, an organization can gain valuable insights into its performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Communication: A KPI tree can be a useful tool for communicating performance data to stakeholders within and outside of the organization. By presenting data in a clear and visual way, it becomes easier to convey key information and insights.
- Continuous improvement: A KPI tree can help to drive continuous improvement within an organization. By regularly monitoring and measuring performance against the most critical KPIs, an organization can identify areas for improvement and make data-driven decisions to optimize its operations.
Building a KPI tree involves several steps:
- Define the overall objective: Start by defining the ultimate goal that your organization is trying to achieve. This should be a clear and specific statement that describes what you are trying to accomplish.
- Identify the critical success factors: Once you have defined the overall objective, identify the factors that are critical to achieving it. These are the high-level areas that you need to focus on to achieve success.
- Break down the critical success factors: For each critical success factor, identify the specific KPIs that will be used to measure performance. These KPIs should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the critical success factor.
- Build the KPI tree: Start by placing the overall objective at the top of the tree. Then, for each critical success factor, add a branch to the tree. Under each branch, add the specific KPIs that are relevant to that critical success factor.
- Organize the KPI tree: Organize the KPI tree in a way that makes sense for your organization. You might group related KPIs together, or you might organize them by department or function.
- Assign ownership and accountability: Assign ownership and accountability for each KPI to a specific individual or team. This helps to ensure that everyone knows who is responsible for each KPI and helps to drive accountability for performance.
- Implement and monitor: Once you have built the KPI tree, implement it within your organization and monitor performance against the KPIs. Regularly review the KPIs and adjust the tree as needed to ensure that it remains relevant and effective.
Remember that building a KPI tree is an iterative process. You may need to make adjustments to the tree over time as you gain more insights into your performance and as your organization evolves.
Schedule a Demo